Eye-tracking technology has emerged as a significant component in the realm of virtual reality (VR), enhancing user experience and interaction. By monitoring where a user is looking, eye-tracking systems can provide insights into attention, engagement, and cognitive load. This data can be invaluable for developers aiming to create more immersive and responsive environments. As VR continues to evolve, the integration of eye-tracking capabilities is becoming increasingly common, allowing for more nuanced interactions and personalized experiences.
The implications of eye-tracking data extend beyond mere user experience. It has the potential to inform design decisions, optimize content delivery, and even influence marketing strategies. However, the collection and use of such data raise important questions about privacy and ethical considerations. As VR technology becomes more mainstream, understanding the nuances of eye-tracking data collection and its implications is crucial for both users and developers alike.
In exploring the privacy implications of eye-tracking data in virtual reality, it is essential to consider how emerging technologies impact user experience and data security. A related article that delves into the intersection of technology and user privacy is titled “Unlock the Power of the Galaxy with the Samsung Galaxy S21.” This article discusses the innovative features of the Samsung Galaxy S21 and raises important questions about data collection and user consent in the context of advanced devices. For more insights, you can read the article here: Unlock the Power of the Galaxy with the Samsung Galaxy S21.
Key Takeaways
- Eye-tracking in VR captures detailed user gaze data to enhance immersive experiences.
- Data is collected via specialized sensors integrated into VR headsets.
- Privacy concerns arise from the sensitive nature of eye-tracking information.
- Misuse risks include unauthorized data sharing and behavioral profiling.
- Legal frameworks and industry standards are evolving to safeguard user privacy in VR.
How Eye-Tracking Data is Collected in VR
Eye-tracking data in VR is typically collected through specialized hardware and software designed to monitor eye movements. This technology often employs infrared light to illuminate the eyes, capturing reflections that indicate where a user is looking. The data is processed in real-time, allowing for immediate feedback within the virtual environment. Various methods exist for eye-tracking, including remote systems that track eye movements from a distance and integrated systems embedded within VR headsets.
The accuracy of eye-tracking data can vary based on several factors, including the quality of the hardware and the calibration process. Calibration usually involves having users focus on specific points within the VR environment to ensure that the system accurately tracks their gaze. Once calibrated, the system can provide detailed information about fixation points, saccades, and gaze patterns, which can be analyzed to understand user behavior and preferences. This data can be used to enhance user interfaces, improve navigation, and create more engaging content.
Privacy Concerns Related to Eye-Tracking Data

As with any technology that collects personal data, eye-tracking in VR raises significant privacy concerns. The ability to monitor where a user is looking can reveal sensitive information about their interests, preferences, and even emotional states. This level of insight poses risks if the data is not handled responsibly. Users may be unaware of how their eye-tracking data is being collected, stored, or utilized, leading to potential breaches of trust between users and developers.
Moreover, the aggregation of eye-tracking data can lead to the creation of detailed profiles that may be used for targeted advertising or other purposes without explicit consent. The potential for misuse increases when considering that this data can be combined with other personal information collected through VR platforms. As such, it is essential for developers and companies to establish clear policies regarding data collection and usage to mitigate privacy risks.
Potential Misuse of Eye-Tracking Data
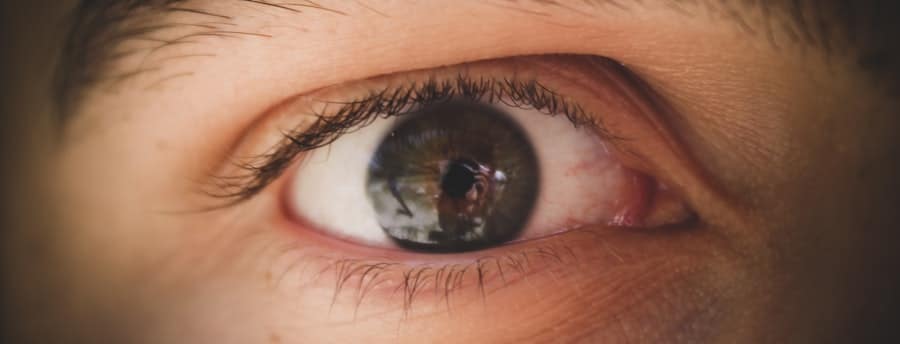
The potential misuse of eye-tracking data in VR environments is a pressing concern for both users and industry stakeholders. One significant risk involves unauthorized access to sensitive information. If eye-tracking data falls into the wrong hands, it could be exploited for malicious purposes, such as identity theft or manipulation of user behavior through targeted advertising. The granularity of the data collected can provide insights that are not only invasive but also potentially harmful if used unethically.
Additionally, there is a risk that companies may prioritize profit over user privacy by leveraging eye-tracking data for aggressive marketing strategies.
For instance, businesses could use this information to create highly targeted advertisements based on users’ gaze patterns and interests.
Such practices could lead to a loss of autonomy for users, as they may find themselves subjected to manipulative marketing tactics that exploit their preferences without their informed consent.
In exploring the complexities of virtual reality, it is essential to consider not only the immersive experiences it offers but also the potential privacy risks associated with technologies like eye-tracking. A related article discusses the importance of safeguarding user data in various digital environments, including how software can enhance home remodeling projects while ensuring user privacy. For more insights on this topic, you can read about it in this informative piece on home remodeling software.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
| Metric | Description | Privacy Implication | Potential Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Granularity | Level of detail in eye-tracking data (e.g., gaze points per second) | High granularity can reveal sensitive user behaviors and preferences | User profiling and behavioral prediction without consent | Data minimization and aggregation before storage |
| Data Retention Period | Duration for which eye-tracking data is stored | Long retention increases risk of unauthorized access | Data breaches exposing personal behavioral data | Implement strict retention policies and automatic deletion |
| Data Sharing | Extent to which eye-tracking data is shared with third parties | Sharing can lead to loss of user control over data | Third-party misuse or re-identification of users | User consent and transparent data sharing agreements |
| Biometric Identification | Use of eye movement patterns to identify individuals | Eye-tracking data can serve as a biometric identifier | Unauthorized tracking and surveillance | Use anonymization and limit biometric data usage |
| Informed Consent | Degree to which users are informed about data collection | Lack of clear consent undermines user autonomy | Legal and ethical violations | Clear, accessible privacy notices and opt-in mechanisms |
| Data Security | Measures to protect eye-tracking data from breaches | Weak security can lead to data leaks | Exposure of sensitive behavioral and biometric data | Encryption, access controls, and regular security audits |
The legal landscape surrounding eye-tracking data in VR is still developing, with many jurisdictions lacking comprehensive regulations specifically addressing this technology. Existing privacy laws may apply, but they often do not account for the unique challenges posed by immersive technologies like VR. For instance, regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe emphasize user consent and data protection but may not fully encompass the nuances of eye-tracking data collection.
Ethically, developers face the challenge of balancing innovation with user rights. The collection of eye-tracking data should be accompanied by transparent practices that inform users about what data is being collected and how it will be used. Ethical considerations also extend to ensuring that users have control over their data, including options for opting out of tracking or deleting their information upon request. Establishing ethical guidelines within the industry can help foster trust between users and developers while promoting responsible use of technology.
Protecting Privacy in VR Environments
To address privacy concerns related to eye-tracking data in VR, developers must implement robust measures to protect user information. One approach involves anonymizing data to prevent the identification of individual users. By aggregating eye-tracking data and removing personally identifiable information, companies can reduce the risk of misuse while still gaining valuable insights into user behavior.
Additionally, providing users with clear options for managing their privacy settings is essential. This includes allowing users to opt out of eye-tracking features or providing them with detailed information about how their data will be used. Transparency in data practices can help build trust and empower users to make informed decisions about their participation in VR environments.
Furthermore, regular audits and assessments of data security practices can help ensure compliance with privacy standards and protect against potential breaches.
Industry Standards and Regulations
As the use of eye-tracking technology in VR becomes more widespread, there is a growing need for industry standards and regulations to govern its use. Various organizations are working towards establishing best practices that prioritize user privacy while promoting innovation in VR technology. These standards may include guidelines on data collection methods, user consent protocols, and security measures for protecting sensitive information.
Regulatory bodies are also beginning to take notice of the implications of emerging technologies like eye tracking in VR. As discussions around privacy continue to evolve, it is likely that new regulations will emerge to address specific concerns related to this technology. Industry stakeholders must stay informed about these developments and actively participate in shaping policies that balance technological advancement with user rights.
Future Implications for Privacy in VR
Looking ahead, the implications of eye-tracking data for privacy in VR are likely to become more complex as technology advances. As VR experiences become increasingly immersive and integrated into daily life, the volume of data collected will grow significantly. This trend raises questions about how companies will manage this information responsibly while ensuring compliance with evolving legal frameworks.
Moreover, as users become more aware of privacy issues related to technology, there may be a demand for greater transparency and control over personal data. Companies that prioritize ethical practices and user empowerment are likely to gain a competitive advantage in an increasingly privacy-conscious market. Ultimately, the future of eye-tracking data in VR will depend on how effectively industry stakeholders address these challenges while fostering innovation that respects user privacy rights.
FAQs
What is eye-tracking technology in VR?
Eye-tracking technology in virtual reality (VR) involves sensors that monitor and record the movement and focus of a user’s eyes within the VR environment. This data helps improve user interaction, rendering efficiency, and immersive experiences.
Why is eye-tracking data considered sensitive information?
Eye-tracking data can reveal detailed insights about a user’s attention, interests, emotional responses, and even health conditions. Because it captures where and how long a person looks at specific elements, it can be used to infer personal preferences and behaviors, raising privacy concerns.
How can eye-tracking data be used beyond improving VR experiences?
Beyond enhancing VR interactions, eye-tracking data can be utilized for targeted advertising, behavioral analytics, and even biometric identification. These uses may lead to privacy risks if data is shared without user consent or used for purposes beyond the original intent.
What are the main privacy risks associated with eye-tracking data in VR?
The primary privacy risks include unauthorized data collection, potential misuse of sensitive behavioral information, lack of transparency about data handling, and insufficient user control over who accesses their eye-tracking data.
How can users protect their privacy when using VR devices with eye-tracking?
Users can protect their privacy by reviewing and adjusting privacy settings, limiting data sharing permissions, using devices from manufacturers with strong data protection policies, and staying informed about how their eye-tracking data is collected, stored, and used.

