In recent years, subscription-based learning models have gained significant traction, reshaping the landscape of education. This shift is largely driven by the increasing demand for flexible, accessible, and affordable learning options. Traditional educational institutions are often constrained by rigid schedules and high tuition fees, making it difficult for many learners to pursue their educational goals.
In contrast, subscription-based models offer a more adaptable approach, allowing students to learn at their own pace and on their own terms. Platforms like Coursera, Udacity, and LinkedIn Learning have emerged as leaders in this space, providing a wide array of courses across various disciplines for a monthly or annual fee. The appeal of subscription-based learning extends beyond mere convenience.
It democratizes education by breaking down geographical and financial barriers that have historically limited access to quality learning resources. For instance, a student in a remote area can now access the same high-quality courses as someone attending a prestigious university in a metropolitan city. This model not only caters to traditional students but also appeals to working professionals seeking to upskill or pivot their careers without the burden of long-term commitments or exorbitant costs.
As a result, subscription-based learning is not just a trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how education is delivered and consumed.
Key Takeaways
- Subscription-based learning models are on the rise, offering flexible and affordable access to educational content and resources.
- Traditional higher education institutions are facing challenges as subscription-based learning models gain popularity, leading to a shift in the education landscape.
- Students benefit from subscription-based learning through access to a wide range of courses, personalized learning experiences, and cost-effective education options.
- Technology plays a crucial role in enabling subscription-based learning, providing platforms for content delivery, interactive learning experiences, and data-driven insights.
- Challenges and concerns for subscription-based learning models include quality control, access to support services, and potential for widening educational inequalities.
The Impact on Traditional Higher Education Institutions
The rise of subscription-based learning models has prompted traditional higher education institutions to reevaluate their offerings and business models. Many universities are beginning to recognize that they must adapt to the changing landscape or risk becoming obsolete. The influx of online courses and programs has led to increased competition, forcing institutions to innovate and enhance their value propositions.
Some universities have started to offer their own subscription-based courses or have partnered with established online platforms to reach a broader audience. This shift reflects an acknowledgment that students are increasingly seeking more flexible and affordable options. Moreover, the financial implications for traditional institutions are significant.
With students opting for subscription-based models, universities may experience declining enrollment numbers, particularly in non-essential programs. This trend can lead to budget cuts, faculty layoffs, and even the closure of certain departments. In response, many institutions are investing in technology and online learning infrastructure to create hybrid models that combine the best of both worlds—traditional classroom experiences with the flexibility of online learning.
This evolution is not merely a reaction to competition; it represents a strategic pivot towards meeting the needs of a diverse student population.
The Benefits for Students
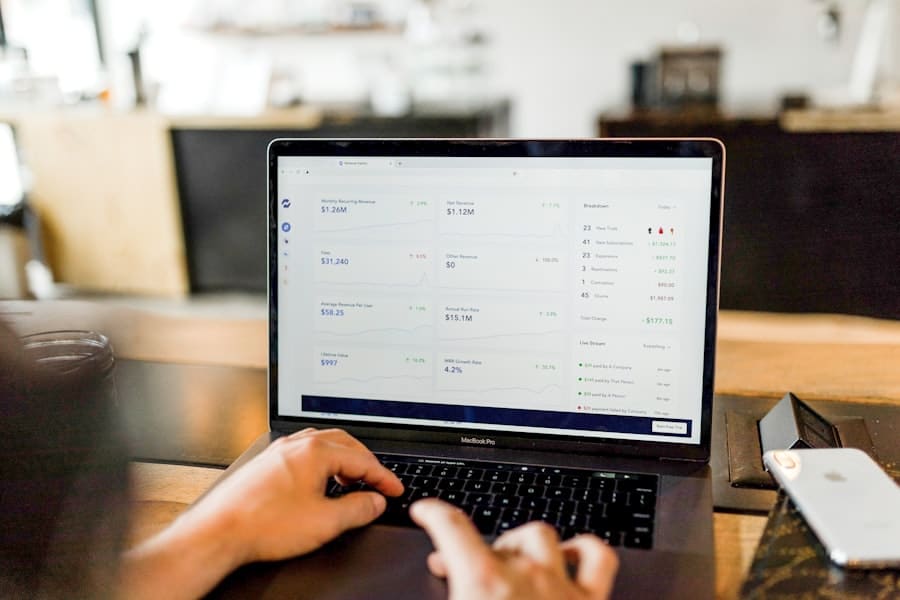

Subscription-based learning models offer numerous benefits for students, making education more accessible and tailored to individual needs. One of the most significant advantages is the flexibility these models provide. Students can choose when and where they want to learn, allowing them to balance their studies with work, family commitments, or other responsibilities.
This flexibility is particularly beneficial for adult learners who may be juggling multiple obligations while trying to advance their careers or pursue new interests. Additionally, subscription-based learning often comes with a wealth of resources that traditional institutions may not provide. Many platforms offer not only courses but also supplementary materials such as quizzes, interactive exercises, and community forums where learners can engage with peers and instructors.
This comprehensive approach fosters a more enriching learning experience, enabling students to deepen their understanding of the subject matter. Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of subscription models allows students to explore various fields without the financial burden associated with enrolling in multiple degree programs. This encourages lifelong learning and exploration, empowering individuals to adapt to an ever-changing job market.
The Role of Technology in Subscription-Based Learning
Technology plays a pivotal role in the success of subscription-based learning models. The proliferation of high-speed internet access and advancements in digital tools have made it possible for educational content to be delivered seamlessly across various devices. Learning management systems (LMS) have evolved significantly, enabling platforms to offer interactive features such as video lectures, discussion boards, and real-time assessments.
These technological innovations enhance the overall learning experience by making it more engaging and interactive. Moreover, data analytics is increasingly being utilized to track student progress and engagement levels within subscription-based platforms. By analyzing user behavior, educators can identify areas where students may be struggling and adjust course content accordingly.
This data-driven approach not only improves course design but also allows for timely interventions that can help students stay on track. As artificial intelligence continues to advance, we can expect even more personalized learning experiences that cater to individual preferences and learning styles, further solidifying the role of technology in shaping the future of education.
Challenges and Concerns for Subscription-Based Learning Models
Despite the numerous advantages associated with subscription-based learning models, several challenges and concerns persist. One major issue is the potential for a lack of accountability and quality assurance in course offerings. With an abundance of courses available online, it can be difficult for students to discern which programs are credible and provide genuine value.
Unlike traditional institutions that are subject to rigorous accreditation processes, many online platforms operate with minimal oversight, raising questions about the quality of education being delivered. Additionally, there is the concern that subscription-based models may inadvertently promote a transactional view of education. When learners pay for access rather than pursuing a degree or certification from an accredited institution, there may be less motivation to engage deeply with the material or complete courses successfully.
This could lead to high dropout rates and a superficial understanding of subjects. Furthermore, while subscription models aim to democratize education, they may still exclude individuals who lack access to technology or reliable internet connections, perpetuating existing inequalities in educational access.
The Potential for Personalized and Adaptive Learning
One of the most promising aspects of subscription-based learning models is their potential for personalized and adaptive learning experiences. Unlike traditional classroom settings where one-size-fits-all approaches often prevail, subscription platforms can leverage technology to tailor educational content to individual learners’ needs. For instance, adaptive learning algorithms can assess a student’s strengths and weaknesses in real-time, adjusting the difficulty level of exercises or suggesting additional resources based on performance.
This level of personalization not only enhances engagement but also fosters a deeper understanding of the material. Students can progress at their own pace, spending more time on challenging concepts while quickly moving through areas they grasp easily. Additionally, personalized feedback mechanisms can provide learners with insights into their progress and areas for improvement, empowering them to take ownership of their educational journey.
The Future of Credentialing and Accreditation
As subscription-based learning models continue to gain prominence, the future of credentialing and accreditation is likely to undergo significant transformation. Traditional degrees have long been viewed as the gold standard for educational attainment; however, as alternative learning pathways emerge, there is growing recognition that skills and competencies should take precedence over formal credentials alone.
This shift raises important questions about how we define educational success and what constitutes a credible qualification in today’s job market. Employers are beginning to prioritize practical skills over degrees from prestigious institutions, leading to a more skills-based hiring approach. As a result, we may see an increase in partnerships between online learning platforms and industry leaders who can help shape curricula that align with current job market demands.
This evolution could ultimately lead to a more dynamic and responsive educational ecosystem that better prepares learners for the realities of modern work.
The Role of Government and Policy in Supporting Subscription-Based Learning Models
The role of government and policy in supporting subscription-based learning models is crucial as these educational innovations continue to evolve. Policymakers have an opportunity to create frameworks that promote equitable access to online education while ensuring quality standards are met across platforms. This could involve establishing guidelines for accreditation processes specific to online courses or incentivizing partnerships between traditional institutions and online providers.
Furthermore, governments can play a vital role in funding initiatives that expand internet access in underserved communities, thereby reducing barriers to participation in subscription-based learning models. By investing in digital infrastructure and supporting digital literacy programs, policymakers can help ensure that all individuals have the opportunity to benefit from these new educational paradigms. As subscription-based learning becomes more integrated into the broader educational landscape, proactive government involvement will be essential in fostering an inclusive environment that prioritizes lifelong learning for all citizens.
In addition to exploring The Future of Subscription-Based Learning Models in Higher Education, readers may also be interested in learning about the best software for 3D printing. This article provides valuable insights into the top software options available for those looking to delve into the world of 3D printing. With the rise of technology in education, understanding the tools and software available for various fields can be crucial for students and professionals alike. Check out the article here for more information.
FAQs
What are subscription-based learning models in higher education?
Subscription-based learning models in higher education are a form of payment where students pay a recurring fee for access to educational resources, courses, and materials. This model allows students to access a variety of learning materials for a set period of time, often on a monthly or yearly basis.
How do subscription-based learning models differ from traditional tuition fees?
Traditional tuition fees require students to pay a fixed amount for each semester or academic year, regardless of the number of courses or resources they use. In contrast, subscription-based learning models offer students access to a wide range of resources for a recurring fee, providing more flexibility and potentially reducing costs for students.
What are the potential benefits of subscription-based learning models in higher education?
Some potential benefits of subscription-based learning models include increased access to educational resources, greater flexibility for students to explore different courses and materials, and potentially lower overall costs for students compared to traditional tuition fees.
What are some challenges or concerns associated with subscription-based learning models?
Challenges and concerns related to subscription-based learning models may include the need to ensure the quality and credibility of the educational resources offered, potential issues with access and equity, and the need to address the financial sustainability of such models for educational institutions.
How are educational institutions and students responding to subscription-based learning models?
Some educational institutions and students are exploring and adopting subscription-based learning models as a way to provide and access educational resources in a more flexible and cost-effective manner. However, there is also ongoing discussion and debate about the potential impact and implications of such models on the higher education landscape.


Add a Comment