The advent of automation in industry marks a significant turning point in the way goods are produced and services are delivered. Over the past few decades, technological advancements have led to the integration of automated systems in various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and even service industries. The rise of automation can be traced back to the introduction of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and robotics in the late 20th century, which laid the groundwork for more sophisticated systems.
Today, automation encompasses a wide range of technologies, from simple conveyor belts to complex artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can learn and adapt to new tasks. As industries strive for efficiency and cost-effectiveness, the push towards automation has accelerated. Companies are increasingly adopting automated solutions to streamline operations, reduce human error, and enhance productivity.
For instance, automotive manufacturers have implemented robotic arms for assembly lines, significantly increasing production rates while maintaining high-quality standards. Similarly, in the logistics sector, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are revolutionizing warehouse operations by optimizing inventory management and reducing the time taken for order fulfillment. This shift towards automation is not merely a trend; it represents a fundamental change in how industries operate, driven by the need for competitiveness in a global market.
Key Takeaways
- Automation is rapidly increasing in industries, leading to changes in job roles and skill requirements.
- Traditional job roles are being impacted by automation, leading to the need for reskilling and upskilling.
- New opportunities are emerging in the field of automation, creating demand for skills in areas such as robotics and data analysis.
- Future career paths will require skills in technology, data analysis, and problem-solving to adapt to the changing industry landscape.
- Artificial intelligence is playing a significant role in driving automation in industries, leading to concerns about job displacement and ethical implications.
Impact on Traditional Job Roles
The integration of automation into various industries has profound implications for traditional job roles. As machines take over repetitive and mundane tasks, many positions that once relied heavily on human labor are becoming obsolete. For example, assembly line jobs in manufacturing have seen a significant decline as robots can perform these tasks more efficiently and without fatigue.
This shift has led to concerns about job displacement, particularly among low-skilled workers who may find it challenging to transition into new roles that require different skill sets. However, the impact of automation on job roles is not solely negative. While certain positions may vanish, others are evolving or emerging altogether.
For instance, the role of a machine operator is transforming into that of a technician who oversees automated systems and ensures their optimal functioning. This evolution necessitates a different set of skills, including technical knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Moreover, as companies invest in automation technologies, there is a growing demand for professionals who can design, program, and maintain these systems.
New Opportunities in Automation
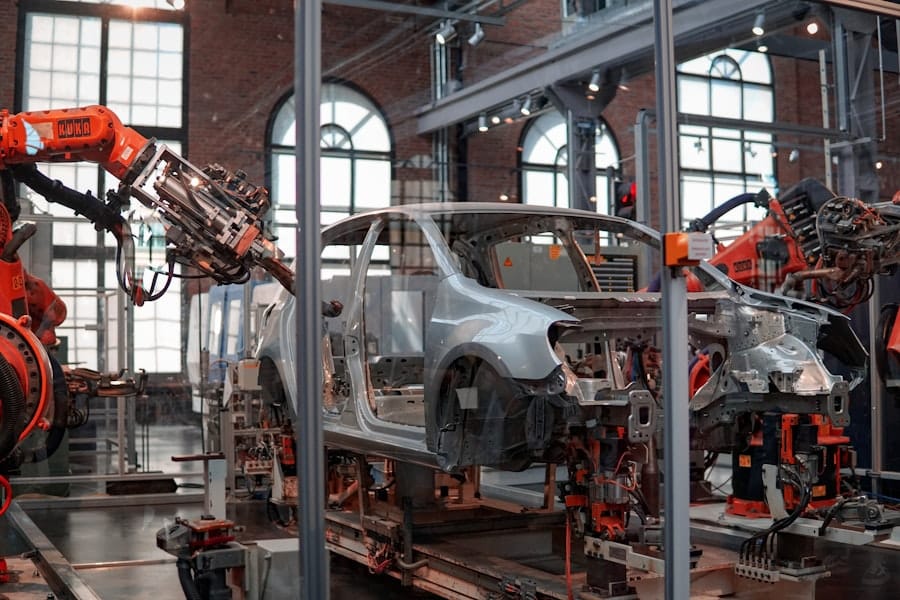

The rise of automation has not only led to the displacement of certain jobs but has also created a plethora of new opportunities across various sectors. As industries embrace automation technologies, there is an increasing need for skilled professionals who can manage and innovate within these automated environments. For instance, roles such as data analysts, robotics engineers, and AI specialists are becoming increasingly vital as companies seek to leverage data-driven insights and advanced technologies to enhance their operations.
In addition to technical roles, there is also a burgeoning demand for professionals in fields such as cybersecurity and system integration. As more devices become interconnected through the Internet of Things (IoT), ensuring the security of these systems becomes paramount. Cybersecurity experts are needed to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of automated processes.
Furthermore, system integrators play a crucial role in ensuring that various automated systems work seamlessly together, highlighting the importance of collaboration between different technological components.
Skills Needed for Future Career Paths
As the landscape of work continues to evolve due to automation, the skills required for future career paths are also changing dramatically. Technical skills related to programming, data analysis, and machine learning are becoming essential for many roles across industries. For example, proficiency in languages such as Python or R is increasingly sought after in fields ranging from finance to healthcare, where data-driven decision-making is paramount.
Understanding how to work with AI algorithms and machine learning models is also becoming a critical competency for those looking to thrive in an automated environment. Beyond technical skills, soft skills are gaining prominence as well. The ability to adapt to new technologies and learn continuously is crucial in an era where change is constant.
Employers are placing a premium on skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence—qualities that machines cannot replicate easily. As automation takes over routine tasks, human workers will need to focus on areas where they can add unique value, such as strategic planning and interpersonal communication.
Reskilling and Upskilling in the Age of Automation
In response to the changing job landscape brought about by automation, reskilling and upskilling have become imperative for both employees and employers. Workers whose roles are at risk due to automation must seek opportunities to acquire new skills that align with emerging job demands. Many organizations are recognizing this need and are investing in training programs designed to help their employees transition into new roles or enhance their existing skill sets.
For instance, companies may offer workshops on programming languages or provide access to online courses focused on data analytics. Moreover, governments and educational institutions are also playing a vital role in facilitating reskilling initiatives. Public-private partnerships are emerging to create training programs that equip individuals with the necessary skills for the future workforce.
For example, coding boot camps have gained popularity as they provide intensive training in programming within a short timeframe. These initiatives not only help individuals adapt to the changing job market but also contribute to building a more resilient economy capable of thriving in an automated world.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Industry
Artificial intelligence is at the forefront of the automation revolution, driving significant changes across various industries. AI technologies enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, making decisions, and learning from experience. In manufacturing, AI-powered predictive maintenance systems can analyze data from machinery to anticipate failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
This capability not only enhances operational efficiency but also extends the lifespan of equipment. In addition to manufacturing, AI is transforming sectors like healthcare by enabling more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data to identify trends and predict patient outcomes with remarkable accuracy.
This application of AI not only improves patient care but also streamlines administrative processes within healthcare organizations. As AI continues to evolve, its potential applications across industries will expand further, leading to even greater efficiencies and innovations.
Challenges and Concerns in the Automation Era
Despite the numerous benefits associated with automation and AI integration into industry, several challenges and concerns persist. One major issue is the potential for increased inequality as certain segments of the workforce may be disproportionately affected by job displacement due to automation. Low-skilled workers are often at greater risk of losing their jobs compared to those with higher education levels or specialized skills.
This disparity raises questions about social equity and access to opportunities in an increasingly automated economy. Another concern revolves around data privacy and security.
High-profile data breaches have highlighted vulnerabilities within automated systems, prompting calls for stricter regulations and enhanced cybersecurity measures. Balancing innovation with ethical considerations will be crucial as organizations navigate the complexities of an automated landscape.
The Future of Work in an Automated Industry
Looking ahead, the future of work in an automated industry will likely be characterized by collaboration between humans and machines rather than outright replacement. While certain jobs may disappear due to automation, new roles will emerge that leverage human creativity and problem-solving abilities alongside advanced technologies. The workplace will increasingly resemble a hybrid environment where humans work alongside AI systems to enhance productivity and drive innovation.
Moreover, as industries continue to evolve, lifelong learning will become a cornerstone of career development. Workers will need to embrace continuous education and adaptability as they navigate an ever-changing job market shaped by technological advancements. Organizations that prioritize employee development through reskilling initiatives will not only foster a more skilled workforce but also cultivate a culture of innovation that thrives in an automated future.
In conclusion, while the rise of automation presents challenges and concerns regarding job displacement and inequality, it also offers new opportunities for growth and innovation across various sectors. By focusing on reskilling and upskilling initiatives while embracing collaboration between humans and machines, industries can navigate this transformative era successfully. The future of work will undoubtedly be shaped by these dynamics as we move towards an increasingly automated world.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, automation is significantly transforming career paths across various industries. A related article that delves into the technological advancements impacting everyday life is What is the Best Tablet to Buy for Everyday Use?. This article explores the latest tablet options that cater to both personal and professional needs, highlighting how these devices are becoming essential tools in an increasingly automated world. As automation continues to reshape industries, staying updated with the best technology for everyday use becomes crucial for adapting to new career demands and enhancing productivity.
FAQs
What is automation in the industry?
Automation in the industry refers to the use of technology and machinery to perform tasks that were previously carried out by humans. This can include processes such as manufacturing, assembly, and even decision-making.
How is automation reshaping career paths in the industry?
Automation is reshaping career paths in the industry by changing the skills and qualifications that are in demand. As more tasks become automated, there is a growing need for workers with technical and digital skills to operate and maintain the automated systems.
What are some examples of careers that are being impacted by automation in the industry?
Some examples of careers that are being impacted by automation in the industry include manufacturing workers, warehouse and logistics professionals, and even white-collar jobs such as data analysis and customer service.
What skills are becoming more important in the age of automation?
In the age of automation, skills such as programming, data analysis, problem-solving, and critical thinking are becoming more important. These skills are essential for operating and troubleshooting automated systems.
What are the potential benefits of automation in the industry?
Some potential benefits of automation in the industry include increased efficiency, higher productivity, improved safety, and the ability to perform repetitive tasks with greater accuracy.
What are the potential challenges of automation in the industry?
Some potential challenges of automation in the industry include job displacement, the need for retraining and upskilling workers, and the potential for increased inequality if certain workers are left behind in the transition to automation.

