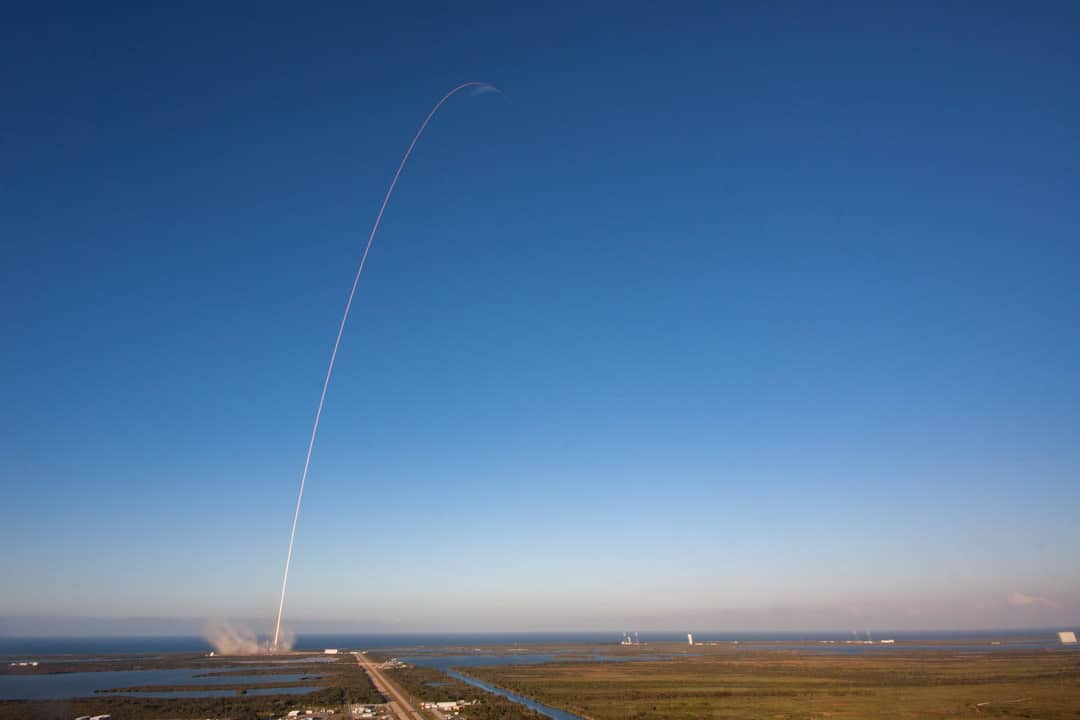
The journey of commercial spaceflight is a fascinating narrative that intertwines technological innovation, entrepreneurial spirit, and the quest for exploration. The roots of commercial spaceflight can be traced back to the mid-20th century, a period marked by the Cold War and the space race between the United States and the Soviet Union. The launch of Sputnik by the USSR in 1957 ignited a fervor for space exploration, leading to significant government investments in aerospace technology.
However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that the concept of commercial spaceflight began to take shape. The establishment of the Space Shuttle program by NASA opened avenues for private companies to engage in space-related activities, albeit primarily as contractors. In the 1990s, the landscape began to shift more dramatically with the advent of private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin.
These companies emerged from a growing recognition that the future of space exploration could be driven by private enterprise rather than solely by government agencies. SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk in 2002, aimed to reduce the cost of space travel and eventually enable human colonization of Mars. The successful launch of the Falcon 1 in 2006 marked a significant milestone, demonstrating that private entities could achieve what was once thought to be the exclusive domain of national governments.
This era laid the groundwork for a new chapter in space exploration, characterized by increased competition and innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Commercial spaceflight has a rich history dating back to the 20th century, with significant milestones achieved by government space agencies and private companies.
- Private companies have played a crucial role in advancing space exploration, with companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin leading the way in developing innovative technologies and reducing costs.
- Advancements in spacecraft technology, such as reusable rockets and advanced propulsion systems, have revolutionized the way we access and explore space.
- Commercial spaceflight has made space more accessible to a wider range of industries and individuals, opening up new opportunities for scientific research, satellite deployment, and space manufacturing.
- The rise of commercial spaceflight has also sparked interest in space tourism, with companies like Virgin Galactic and SpaceX aiming to offer suborbital and orbital spaceflights to private individuals in the near future.
The Role of Private Companies in Space Exploration
Private companies have become pivotal players in the realm of space exploration, fundamentally altering how missions are conceived, funded, and executed. Unlike traditional government-led initiatives, which often face bureaucratic hurdles and budget constraints, private enterprises can operate with greater agility and flexibility. This shift has led to a surge in innovative approaches to space travel, with companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic leading the charge.
These firms have not only developed advanced spacecraft but have also introduced new business models that prioritize cost-effectiveness and efficiency. The role of private companies extends beyond mere transportation; they are also involved in research and development, satellite deployment, and even planetary exploration. For instance, SpaceX’s partnership with NASA for the Commercial Crew Program has revolutionized how astronauts are transported to the International Space Station (ISS).
By providing reliable and cost-effective transportation solutions, private companies have alleviated some of the financial burdens on government agencies while simultaneously enhancing mission capabilities. Furthermore, these companies are increasingly collaborating with international space agencies, fostering a spirit of cooperation that transcends national boundaries.
Advancements in Spacecraft Technology
The advancements in spacecraft technology over the past two decades have been nothing short of revolutionary. Innovations in materials science, propulsion systems, and avionics have significantly enhanced the capabilities of modern spacecraft. For example, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket features reusable first-stage boosters that can land back on Earth after launch, drastically reducing costs associated with space travel.
This reusability paradigm is a game-changer; it allows for more frequent launches and opens up new possibilities for commercial ventures in space. Moreover, advancements in satellite technology have transformed how we communicate and gather data from space. The deployment of small satellites, or CubeSats, has democratized access to space for universities and startups alike.
These miniature satellites can be launched at a fraction of the cost of traditional satellites, enabling a wide range of applications from Earth observation to scientific research. Additionally, developments in propulsion technology, such as ion thrusters and solar sails, promise to extend our reach within the solar system and beyond. These innovations not only enhance our capabilities but also inspire new generations of engineers and scientists to push the boundaries of what is possible.
The Impact of Commercial Spaceflight on Accessibility
One of the most profound impacts of commercial spaceflight is its potential to enhance accessibility to space for a broader range of stakeholders. Historically, access to space was limited to government astronauts and select researchers; however, the emergence of commercial spaceflight has begun to change this narrative. Companies like Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic are actively working to make suborbital flights available to civilians, allowing individuals from various backgrounds to experience weightlessness and view Earth from above.
This democratization of space travel is not merely about providing a unique experience; it also has implications for education and inspiration. As more people venture into space, they return with stories that captivate audiences worldwide. This phenomenon can ignite interest in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) fields among young people who aspire to be part of this burgeoning industry.
Furthermore, as commercial spaceflight becomes more mainstream, it could lead to a cultural shift where space exploration is viewed as an attainable goal rather than an exclusive privilege reserved for a select few.
Opportunities for Space Tourism
Space tourism represents one of the most exciting frontiers within commercial spaceflight. The concept has transitioned from science fiction to reality as companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin prepare to offer suborbital flights to paying customers. These experiences promise not only breathtaking views of Earth but also a taste of microgravity that few have experienced before.
The burgeoning market for space tourism is indicative of a broader trend where adventure-seeking individuals are willing to invest significantly for unique experiences. The potential economic impact of space tourism is substantial. As ticket prices decrease over time due to advancements in technology and increased competition among providers, it is anticipated that more people will be able to afford these journeys.
This could lead to a thriving industry that generates jobs in various sectors, including hospitality, training, and aerospace engineering. Additionally, as public interest grows, there may be opportunities for ancillary services such as pre-flight training programs or themed experiences that cater to aspiring space tourists.
The Future of Commercial Spaceflight
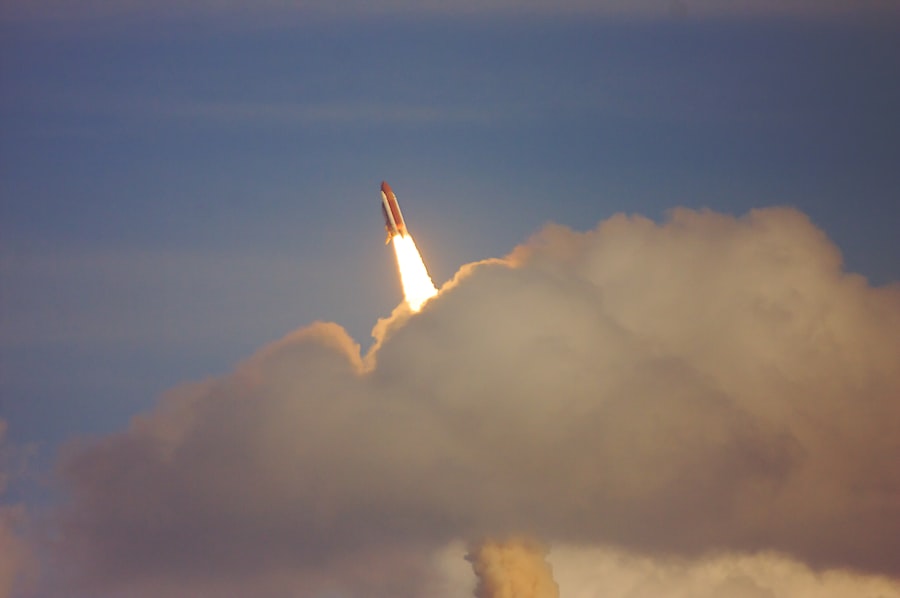

Looking ahead, the future of commercial spaceflight appears promising yet complex. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, we can expect new players to enter the market alongside established giants like SpaceX and Blue Origin. This influx of competition will likely drive innovation further while also lowering costs for consumers.
Moreover, as international collaboration becomes more common in space endeavors, we may witness joint missions involving multiple private companies and government agencies working together toward shared goals. The vision for commercial spaceflight extends beyond mere tourism; it encompasses ambitious projects such as lunar bases and Mars colonization efforts. Companies are already laying the groundwork for lunar missions through initiatives like NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon by 2024 with significant involvement from private contractors.
The prospect of establishing a sustainable human presence on other celestial bodies could redefine humanity’s relationship with space and open up new avenues for exploration and resource utilization.
Challenges and Risks of Commercial Spaceflight
Despite its many advantages, commercial spaceflight is not without challenges and risks that must be addressed as the industry matures. Safety remains a paramount concern; even minor failures can have catastrophic consequences when human lives are at stake. The tragic accidents involving SpaceShipTwo in 2014 and more recently during test flights underscore the inherent dangers associated with launching spacecraft into orbit or beyond.
As private companies push the boundaries of technology and innovation, they must prioritize rigorous safety protocols and transparent reporting practices. Regulatory hurdles also pose significant challenges for commercial spaceflight ventures. Navigating the complex landscape of international laws governing airspace and outer space can be daunting for new entrants into the market.
Additionally, issues related to orbital debris management are becoming increasingly pressing as more satellites are launched into low Earth orbit (LEO). The potential for collisions between satellites or with other spacecraft necessitates comprehensive strategies for debris mitigation and management.
The Economic and Social Benefits of Commercial Spaceflight
The economic implications of commercial spaceflight extend far beyond immediate job creation within aerospace companies. The industry has catalyzed growth across various sectors by fostering innovation in materials science, telecommunications, and robotics. For instance, advancements made in developing lightweight materials for spacecraft have applications in automotive manufacturing and consumer electronics.
Furthermore, satellite technology has revolutionized global communications and data collection processes across industries ranging from agriculture to disaster response. Socially, commercial spaceflight has the potential to inspire a new generation of explorers and innovators who view space as an accessible frontier rather than an unattainable dream. Educational initiatives tied to commercial missions can engage students in hands-on learning experiences that spark curiosity about science and technology.
As more individuals participate in or witness human activities in space—whether through tourism or scientific research—the collective consciousness surrounding our place in the universe may shift dramatically. This cultural transformation could foster greater appreciation for Earth’s resources while encouraging collaborative efforts toward sustainable practices both on our planet and beyond. In summary, commercial spaceflight represents a dynamic intersection of history, technology, economics, and human aspiration.
As we stand on the brink of a new era in exploration—one characterized by private enterprise driving innovation—the possibilities seem boundless. The journey ahead will undoubtedly be filled with challenges; however, it is also ripe with opportunities that promise to reshape our understanding of what it means to explore beyond our home planet.
In the context of the burgeoning commercial spaceflight industry, it’s essential to consider the technological advancements that support this sector. A related article that delves into another aspect of modern technology is “How Smartwatches are Revolutionizing the Workplace.” This piece explores how wearable technology, like smartwatches, is transforming efficiency and communication in professional settings. For those interested in how technological innovations are reshaping various industries, including how they might impact space travel indirectly by enhancing communication and monitoring capabilities, this article is a must-read. You can find it here: How Smartwatches are Revolutionizing the Workplace.
FAQs
What is commercial spaceflight?
Commercial spaceflight refers to the use of privately funded and operated spacecraft for the purpose of transporting cargo, satellites, and humans to and from space. This is in contrast to government-funded space programs, such as NASA, which have historically been the primary entities involved in space exploration.
How has commercial spaceflight made space more accessible?
Commercial spaceflight has made space more accessible by driving down the cost of launching payloads into space. This has been achieved through innovations in technology, streamlined operations, and competition among private companies. As a result, more organizations and individuals are able to afford access to space for scientific research, satellite deployment, and even tourism.
What are some notable achievements in commercial spaceflight?
Some notable achievements in commercial spaceflight include the development of reusable rockets by companies like SpaceX, the successful deployment of satellite constellations by companies like OneWeb and SpaceX, and the transportation of astronauts to the International Space Station by SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft.
What are the key players in the commercial spaceflight industry?
Some key players in the commercial spaceflight industry include SpaceX, Blue Origin, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman. These companies are actively involved in developing and operating spacecraft for various purposes, including cargo resupply missions, satellite launches, and crewed spaceflights.
What are the potential future developments in commercial spaceflight?
The future of commercial spaceflight holds the promise of increased collaboration with international partners, the expansion of space tourism, the development of lunar and Mars exploration missions, and the continued advancement of reusable rocket technology. Additionally, the potential for commercial space stations and in-space manufacturing could further expand the accessibility and utilization of space.

