The advent of technology has revolutionized the educational landscape, giving rise to virtual classrooms that transcend geographical boundaries and traditional learning environments. Virtual classrooms are online platforms that facilitate real-time interaction between educators and students, allowing for a dynamic exchange of knowledge and ideas. These digital spaces have become increasingly popular, especially in the wake of global events that necessitated remote learning solutions.
They offer a flexible and accessible alternative to conventional classrooms, enabling learners to engage with course materials and instructors from virtually anywhere in the world. In essence, virtual classrooms combine various multimedia tools, such as video conferencing, interactive whiteboards, and discussion forums, to create an immersive learning experience. This innovative approach not only caters to diverse learning styles but also fosters collaboration among students.
As educational institutions continue to embrace this model, understanding the intricacies of virtual classrooms becomes essential for educators aiming to optimize student engagement and learning outcomes. The focus on analyzing student progress within these environments is particularly crucial, as it provides insights into individual and collective performance, ultimately guiding instructional strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Virtual classrooms provide a digital platform for remote learning and interaction between students and teachers.
- Virtual classrooms offer a variety of tools and features for analyzing student progress, such as attendance tracking, assignment submissions, and performance analytics.
- Analyzing student progress in virtual classrooms allows for personalized learning, early intervention, and data-driven decision making.
- The benefits of using virtual classrooms for analyzing student progress include increased student engagement, improved teacher-student communication, and access to real-time performance data.
- Challenges and limitations of analyzing student progress in virtual classrooms include technology barriers, privacy concerns, and the need for effective data interpretation and action planning.
The Role of Virtual Classrooms in Education
Real-Time Learning for Immediate Feedback
In synchronous learning, students and instructors interact simultaneously through live lectures or discussions, mimicking traditional classroom dynamics.
Flexible Learning for Diverse Needs
On the other hand, asynchronous learning provides flexibility, enabling students to access recorded lectures, complete assignments at their own pace, and participate in discussion boards without the constraints of a fixed schedule. This dual approach caters to a wide range of learners, accommodating those who thrive in structured environments as well as those who prefer self-directed study.
Personalized Learning through Technology
Virtual classrooms facilitate personalized learning experiences by leveraging technology to tailor educational content to individual needs. Educators can utilize data analytics tools to track student engagement and performance metrics, allowing them to identify areas where students may struggle. This data-driven approach enables instructors to modify their teaching strategies, provide targeted interventions, and enhance overall student success.
Tools and Features for Analyzing Student Progress
Analyzing student progress in virtual classrooms requires a suite of specialized tools and features designed to capture and interpret various data points. Learning Management Systems (LMS) such as Canvas, Moodle, and Blackboard are integral to this process. These platforms offer functionalities that allow educators to track attendance, monitor assignment submissions, and assess quiz results.
By aggregating this data, instructors can gain insights into student engagement levels and academic performance over time. In addition to LMS platforms, many virtual classrooms incorporate analytics dashboards that visualize student progress through graphs and charts. These dashboards can display metrics such as participation rates in discussions, completion rates for assignments, and overall grades.
Furthermore, some systems employ adaptive learning technologies that adjust content delivery based on individual student performance. For instance, if a student consistently struggles with a particular topic, the system may recommend additional resources or exercises tailored to reinforce that area of knowledge. Such tools not only streamline the analysis process but also provide actionable insights that can inform instructional decisions.
Benefits of Using Virtual Classrooms for Analyzing Student Progress
The benefits of utilizing virtual classrooms for analyzing student progress are manifold. One significant advantage is the ability to collect real-time data on student performance. Unlike traditional classrooms where feedback may be delayed until the end of a term or semester, virtual classrooms enable educators to monitor progress continuously.
This immediacy allows for timely interventions when students exhibit signs of struggle or disengagement, fostering a proactive approach to education. Additionally, virtual classrooms promote a more inclusive learning environment by accommodating diverse learning preferences. For instance, visual learners may benefit from video content and infographics, while auditory learners might excel through podcasts or live discussions.
By analyzing student progress through various lenses—such as participation in different types of activities—educators can identify which methods resonate most with their students. This tailored approach not only enhances individual learning experiences but also contributes to improved overall class performance.
Challenges and Limitations of Analyzing Student Progress in Virtual Classrooms
Despite the advantages of virtual classrooms in analyzing student progress, several challenges and limitations persist. One primary concern is the potential for data overload. With an abundance of metrics available—from attendance rates to assignment scores—educators may find it overwhelming to sift through information and extract meaningful insights.
This complexity can lead to analysis paralysis, where instructors struggle to make informed decisions due to the sheer volume of data at their disposal. Another significant challenge is ensuring data accuracy and reliability. In virtual environments, factors such as technical issues or varying levels of student engagement can skew results.
For example, a student may log into a session but remain passive or distracted, leading to inflated attendance figures without corresponding engagement levels. Additionally, disparities in access to technology can create inequities in data collection; students with limited internet connectivity may not participate fully in online assessments or discussions, resulting in incomplete or misleading data about their progress.
Strategies for Effective Analysis of Student Progress in Virtual Classrooms
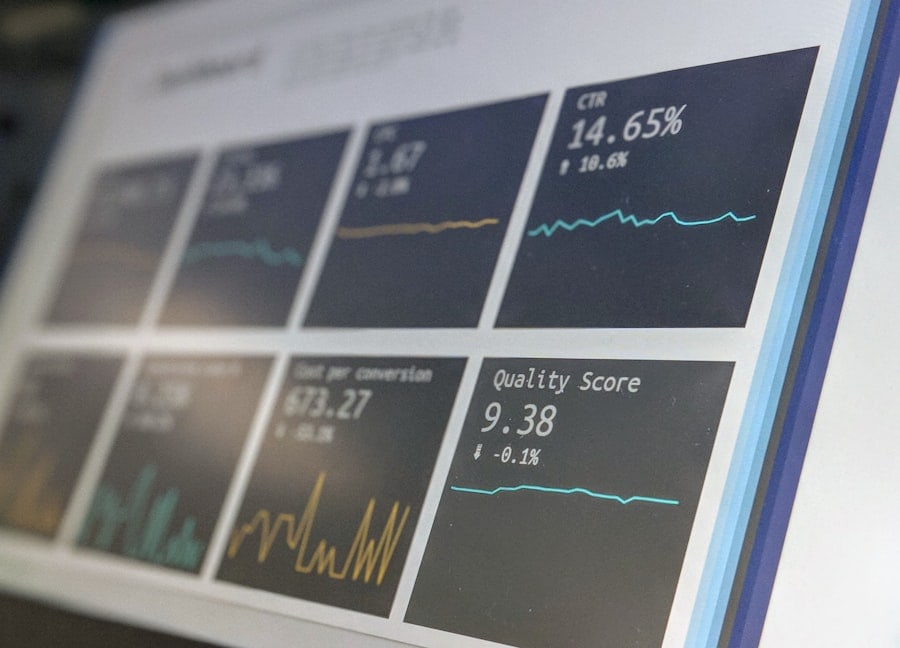
Establishing Clear Learning Objectives
First and foremost is the establishment of clear learning objectives aligned with assessment criteria. By defining specific goals for each course or module, instructors can create targeted assessments that measure student understanding accurately. This clarity not only guides students in their learning journey but also provides a framework for evaluating their progress.
Formative Assessments for Ongoing Insights
Incorporating formative assessments throughout the course is another effective strategy. Unlike summative assessments that evaluate cumulative knowledge at the end of a term, formative assessments—such as quizzes, polls, or reflective journals—offer ongoing insights into student comprehension. These assessments can be designed to provide immediate feedback, allowing students to identify areas for improvement while enabling educators to adjust their teaching methods accordingly.
Fostering Open Communication and Holistic Analysis
Furthermore, fostering open communication channels between students and instructors is crucial for effective analysis. Regular check-ins through one-on-one meetings or feedback sessions can help educators gauge student sentiment and engagement levels beyond quantitative metrics. This qualitative data complements numerical assessments and provides a more holistic view of student progress.
Case Studies and Examples of Successful Student Progress Analysis in Virtual Classrooms
Numerous educational institutions have successfully implemented strategies for analyzing student progress within virtual classrooms, yielding positive outcomes. For instance, Arizona State University (ASU) adopted an innovative approach by integrating predictive analytics into its online courses. By analyzing historical data on student performance and engagement patterns, ASU developed algorithms that identify at-risk students early in the semester.
This proactive intervention strategy has led to increased retention rates and improved academic performance among students who might otherwise have struggled. Another compelling example comes from the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), which utilized a combination of LMS analytics and personalized feedback mechanisms in its online nursing program. Instructors employed data visualization tools to track student participation in discussions and assignment submissions closely.
By providing tailored feedback based on individual performance metrics, UIC was able to enhance student engagement significantly. The program reported higher completion rates and improved overall satisfaction among students who felt more supported throughout their learning experience.
Future Trends and Developments in Virtual Classrooms for Analyzing Student Progress
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of virtual classrooms in analyzing student progress. One emerging trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into educational platforms. AI-driven analytics can provide deeper insights into student behavior by identifying patterns that may not be immediately apparent through traditional analysis methods.
For instance, machine learning algorithms could predict future performance based on past behavior, allowing educators to tailor interventions more effectively. Additionally, the rise of gamification in education presents new opportunities for engaging students while simultaneously tracking their progress. By incorporating game-like elements into assessments—such as badges for achievements or leaderboards for participation—educators can motivate students while collecting valuable data on their engagement levels and mastery of content.
Moreover, advancements in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies hold promise for creating immersive learning experiences that facilitate real-time assessment of student skills and competencies. These technologies could enable educators to observe students in simulated environments, providing insights into their problem-solving abilities and collaborative skills in ways that traditional assessments cannot capture. In conclusion, the future of virtual classrooms is poised for exciting developments that will enhance the analysis of student progress further.
As educational institutions continue to embrace these innovations, they will be better equipped to support diverse learners and foster academic success in an increasingly digital world.
In addition to utilizing virtual classrooms to analyze student progress, educators can also benefit from choosing the right technology to enhance their teaching methods. An article on com/how-to-choose-laptop-for-students/’>how to choose a laptop for students provides valuable insights into selecting the best device for educational purposes.
By investing in the right tools, educators can further optimize their virtual teaching experience and effectively track student progress.
FAQs
What are virtual classrooms?
Virtual classrooms are online learning environments that allow educators and students to interact in real time through video conferencing, chat, and other digital tools. These platforms are designed to mimic the experience of a traditional classroom, but in a virtual setting.
How do virtual classrooms help educators analyze student progress?
Virtual classrooms provide educators with tools to track and monitor student participation, engagement, and performance. They can use features such as attendance tracking, online quizzes and assignments, and real-time feedback to assess student progress and identify areas for improvement.
What data can educators gather from virtual classrooms to analyze student progress?
Educators can gather data on student attendance, participation in class discussions, completion of assignments, quiz and test scores, and overall engagement with the learning materials. This data can help educators identify patterns and trends in student performance and make informed decisions about their teaching strategies.
How do virtual classrooms support personalized learning and individualized feedback?
Virtual classrooms allow educators to provide personalized learning experiences by tailoring instruction to meet the specific needs and learning styles of each student. They can also use the data collected from virtual classrooms to provide individualized feedback and support to students based on their progress and performance.
What are some challenges of using virtual classrooms to analyze student progress?
Some challenges of using virtual classrooms to analyze student progress include ensuring equitable access to technology and internet connectivity for all students, addressing privacy and security concerns related to online learning platforms, and effectively managing and interpreting the large amount of data generated from virtual classrooms.

