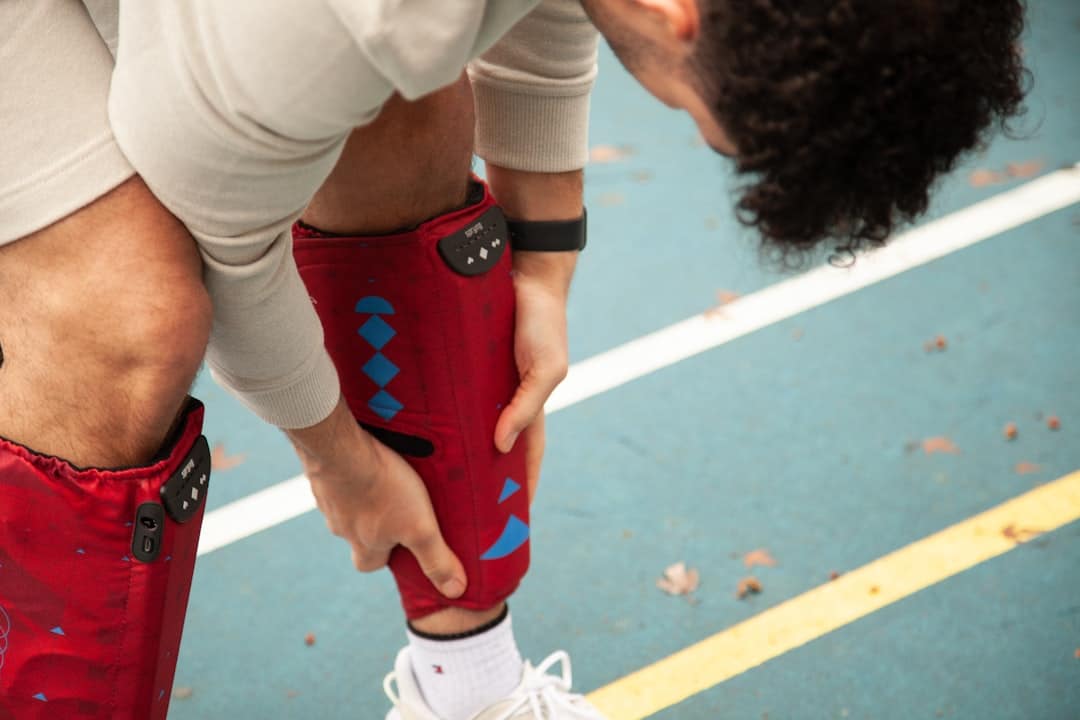
Wearable technology has transformed multiple industries, including healthcare. In post-surgical recovery, wearable devices serve as essential monitoring tools that track patient progress, support recovery processes, and enhance healthcare delivery systems. These devices encompass smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical sensors that collect and process health-related data.
Through continuous monitoring capabilities, wearables provide healthcare professionals and patients with real-time health information during the post-operative recovery period. The incorporation of wearable technology into post-surgical care protocols represents a transition toward data-driven, personalized healthcare approaches. Conventional recovery monitoring typically depends on scheduled medical appointments and patient-reported symptoms, creating potential information gaps and missed clinical indicators.
Wearable devices address these limitations through continuous health metric tracking, enabling healthcare providers to implement preventive interventions and adjust treatment plans based on objective data. Healthcare systems are increasingly adopting digital health technologies, with wearables playing an expanding role in post-operative patient management and clinical outcome improvement.
Key Takeaways
- Wearable devices play a crucial role in monitoring and supporting patients during post-surgery recovery.
- They help track physical activity, vital signs, and medication adherence to ensure optimal healing.
- Real-time feedback from wearables enhances patient engagement and motivation throughout recovery.
- Integration of wearable data into healthcare systems improves personalized care and clinical decision-making.
- Future advancements and challenges include data privacy, device accuracy, and broader adoption in medical practice.
Monitoring Physical Activity and Exercise
One of the most critical aspects of post-surgery recovery is the gradual resumption of physical activity. Wearable devices play a crucial role in this process by tracking a patient’s movement and exercise levels. For instance, devices equipped with accelerometers can measure steps taken, distance traveled, and even the intensity of physical activity.
This data is invaluable for healthcare providers who need to assess whether patients are adhering to prescribed rehabilitation protocols. By monitoring activity levels, clinicians can tailor exercise regimens to individual needs, ensuring that patients do not overexert themselves while also encouraging them to remain active. Moreover, wearables can provide insights into specific types of exercises that are beneficial for recovery.
For example, after orthopedic surgery, patients may be advised to engage in low-impact activities such as walking or cycling. Wearable devices can track these activities and provide feedback on performance, helping patients understand their progress over time. Additionally, some wearables come with built-in coaching features that guide users through rehabilitation exercises, ensuring they perform movements correctly and safely.
This real-time feedback not only enhances the effectiveness of rehabilitation but also fosters a sense of accountability among patients.
Tracking Vital Signs and Health Metrics

Wearable technology has advanced significantly in its ability to monitor vital signs and other health metrics. Devices can now track heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and even body temperature with remarkable accuracy. This continuous monitoring is particularly beneficial in the post-surgical context, where fluctuations in vital signs can indicate complications or the need for medical intervention.
The data collected by wearables can be transmitted directly to healthcare professionals, allowing for timely interventions when necessary. This capability is especially crucial for patients who may be at higher risk for complications following surgery.
For example, patients who have undergone major surgeries may experience changes in their cardiovascular status that could go unnoticed without continuous monitoring. By leveraging wearable technology, healthcare providers can maintain a vigilant watch over their patients’ health, leading to quicker responses and potentially better outcomes.
Managing Medication Adherence
Medication adherence is a significant challenge in post-surgery recovery, as patients often struggle to keep track of their prescriptions and dosing schedules. Wearable devices can play a pivotal role in addressing this issue by providing reminders and alerts for medication intake. Some advanced wearables are even equipped with features that allow them to sync with medication management apps, ensuring that patients receive timely notifications about when to take their medications.
This integration helps reduce the risk of missed doses, which can adversely affect recovery. In addition to reminders, wearables can also track medication adherence by logging when doses are taken. This data can be invaluable for healthcare providers who need to assess whether patients are following their prescribed regimens.
For instance, if a patient consistently misses doses, clinicians can intervene by discussing potential barriers to adherence or adjusting the treatment plan as necessary. By facilitating better medication management through wearables, healthcare systems can enhance patient safety and improve overall recovery outcomes.
Providing Real-Time Feedback and Support
| Metric | Description | Typical Range/Value | Role in Post-Surgery Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate Monitoring | Continuous tracking of heartbeats per minute | 60-100 bpm (resting) | Detects abnormal heart rates indicating complications or stress |
| Step Count | Number of steps taken daily | 500-5000 steps (varies by recovery stage) | Monitors mobility progress and encourages gradual increase in activity |
| Sleep Quality | Duration and restfulness of sleep cycles | 7-9 hours, with REM and deep sleep phases | Assesses recovery quality and helps identify pain or discomfort |
| Oxygen Saturation (SpO2) | Percentage of oxygen in the blood | 95-100% | Ensures adequate oxygenation, critical for healing |
| Body Temperature | Continuous or periodic measurement of body heat | 36.1-37.2 °C (97-99 °F) | Detects fever or infection early in recovery |
| Pain Level Reporting | Patient input on pain intensity via wearable interface | Scale 0-10 | Helps tailor pain management and medication adjustments |
| Respiratory Rate | Number of breaths per minute | 12-20 breaths/min | Monitors respiratory function and detects distress |
| Activity Duration | Total time spent in physical activity daily | Varies by recovery protocol | Tracks adherence to rehabilitation exercises |
The ability of wearables to provide real-time feedback is one of their most significant advantages in post-surgery recovery. Patients often have questions or concerns about their recovery process, and wearable devices can offer immediate answers based on collected data. For example, if a patient is unsure whether they are engaging in enough physical activity or if they are experiencing unusual symptoms, they can consult their wearable device for insights into their current health status.
This immediate access to information can alleviate anxiety and empower patients to take an active role in their recovery. Furthermore, many wearables come equipped with communication features that allow patients to connect directly with their healthcare providers. This capability fosters a collaborative approach to recovery, where patients feel supported and engaged throughout the process.
For instance, if a patient experiences discomfort during rehabilitation exercises, they can quickly relay this information to their clinician via the wearable device. This real-time communication enables healthcare providers to make timely adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the support they need when they need it most.
Enhancing Patient Engagement and Motivation
Wearable technology has the potential to significantly enhance patient engagement and motivation during post-surgery recovery. By providing tangible data on progress—such as steps taken or calories burned—wearables can help patients visualize their recovery journey. This visualization serves as a powerful motivator; seeing incremental improvements can encourage patients to adhere to their rehabilitation protocols and maintain an active lifestyle.
For example, a patient recovering from knee surgery may find motivation in tracking their daily step count and striving to surpass previous records. Additionally, many wearable devices incorporate gamification elements that make the recovery process more engaging. Features such as challenges, rewards for achieving milestones, or social sharing capabilities can create a sense of community among users.
Patients may feel more motivated to participate in their recovery when they know they are part of a larger group working towards similar goals. This sense of camaraderie can be particularly beneficial for individuals who may feel isolated during their recovery journey.
Integrating Wearable Data into Healthcare Systems
The integration of wearable data into existing healthcare systems presents both opportunities and challenges for improving post-surgery recovery outcomes. As healthcare providers increasingly recognize the value of continuous monitoring through wearables, there is a growing need for systems that can seamlessly incorporate this data into electronic health records (EHRs). By doing so, clinicians can gain a comprehensive view of a patient’s health status over time, allowing for more informed decision-making.
However, integrating wearable data into healthcare systems also raises concerns regarding data privacy and security. As sensitive health information is transmitted between devices and healthcare providers, it is essential to implement robust security measures to protect patient data from unauthorized access or breaches. Additionally, standardizing data formats across different wearable devices will be crucial for ensuring compatibility with EHR systems.
Addressing these challenges will require collaboration between technology developers, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies to create frameworks that prioritize both innovation and patient safety.
Future Opportunities and Challenges for Wearables in Post-Surgery Recovery
The future of wearables in post-surgery recovery holds immense promise as technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace. Innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning could further enhance the capabilities of wearable devices by enabling predictive analytics based on collected health data. For instance, AI algorithms could analyze patterns in vital signs or activity levels to identify potential complications before they become critical issues.
Despite these opportunities, several challenges remain on the horizon for the widespread adoption of wearables in post-surgery recovery. One significant hurdle is ensuring equitable access to technology across diverse patient populations.
While wearables have become more affordable over time, disparities in access to technology may persist among different socioeconomic groups. Additionally, there is a need for ongoing education and training for both patients and healthcare providers regarding the effective use of wearable technology in clinical practice. As the landscape of healthcare continues to evolve with the integration of digital solutions like wearables, it is essential for stakeholders to collaborate in addressing these challenges while harnessing the potential benefits that these technologies offer for post-surgery recovery.
The journey towards fully realizing the capabilities of wearables in enhancing patient care is ongoing; however, the commitment to innovation and improvement remains steadfast within the healthcare community.
In addition to exploring the role of wearables in post-surgery recovery, you may find it interesting to read about the latest advancements in smartwatch technology, which can significantly enhance health monitoring during recovery. For more insights, check out the article on

